Quote
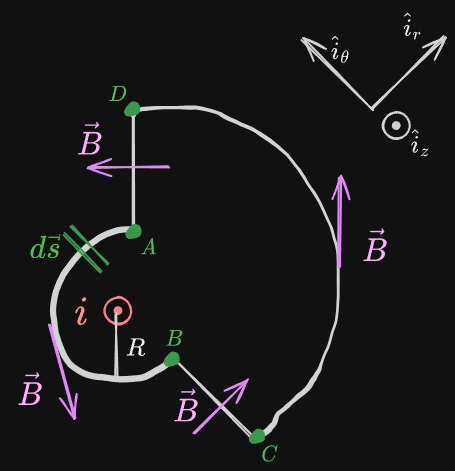
Ampere’s Law states that for any closed loop path, the sum of the length elements times The Magnetic Field in the direction of the length element is equal to the permeability times the electric Current enclosed in the loop.
We use imaginary Amperian loops to determine the magnetic field from a surface. It is similar to Gauss’s Law.
The Differential Form of Ampere’s Law is
This is not actually Ampere’s Law! Maxwell added a term for Displacement Current, so the complete Ampere’s Law is
Some examples:
Along a Long Straight Current Carrying Wire:
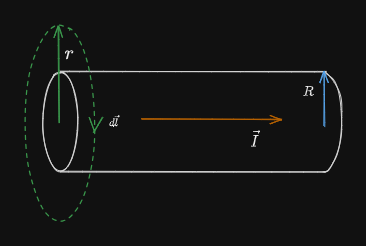
We form an Amperian loop (green) with radius
Inside a Long Straight Current Carrying Wire
This is the same as before, but this time
Since we aren’t using the whole current
We use this in Ampere’s Law:
Radially Shaped Wire