Coulomb’s Law gives the electrostatic force between two particles:
Where
We often use
You can check the direction of force using the Fundamental Law of Charges.
In terms of The Electric Field,
Coulomb’s Law is an application of Gauss’s Law for force between two particles.
In electromagnetism, if you have more than one charge acting on a particle, you can just add the charges. This is not true for all forces (for example, the strong nuclear force). It is from this principle that we can perform calculus for Distributed Charges on Objects.
Example. Find the coulomb force on 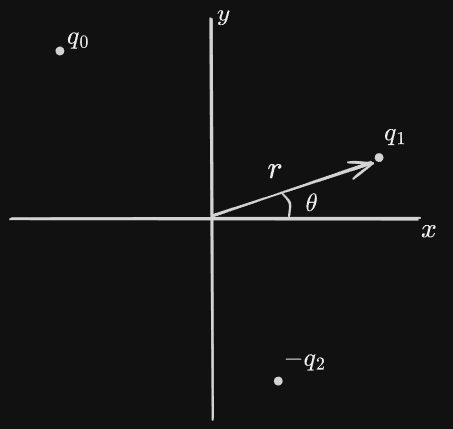
Description: we have three point charges.
The total force on
We can find
Let’s rewrite our vectors to make the problem easier:
So
We can split this into