Wires and loops can experience net forces as a result of changing Magnetic Flux. If those forces are unbalanced, they will have a linear acceleration, and if the Torques are unbalanced, they will have a rotational acceleration.
This is the principle behind electric motors. A coil Rotates in a Magnetic Field from a net torque, and the spinning is harnessed for various applications.
For example:
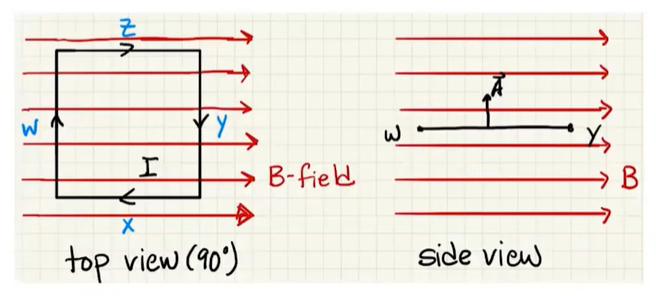
For sides
For side
We now see that the forces cancel (
If we shift the angle so that the loop is at a 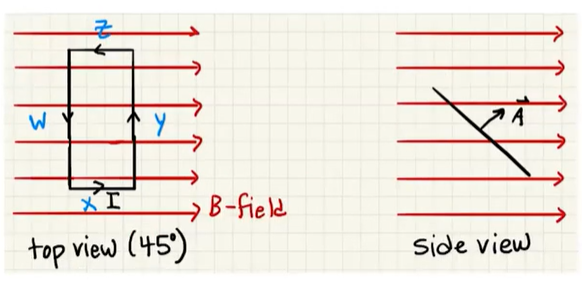
There will still be a net force of zero. However, the net torque will be smaller.
When the angle between 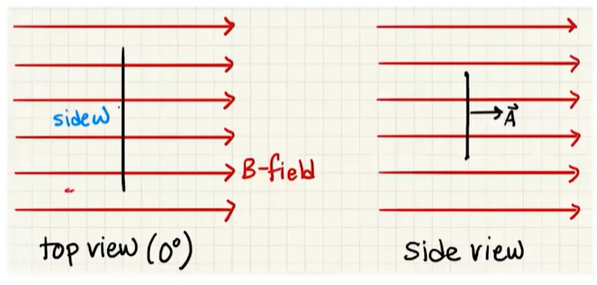
The net force is still zero since the net force on opposite sides are zero. The net torque is also zero here; using the right hand rule, we can see that there is an outward force on each wire.