Gauss’s Law states that the net Electric Flux through any imaginary closed surface is equal to the net charge enclosed within that surface divided by
We can use the Electric Flux equation to make this more useful:
The integral here is a closed integral, which is just a notation that says that we are using a closed surface.
Note that these are imaginary surfaces, and are not meant to be surfaces that actually exist. By manipulating these imaginary surfaces, we can find information about electric field and charge.
We get our equation for enclosed charge over 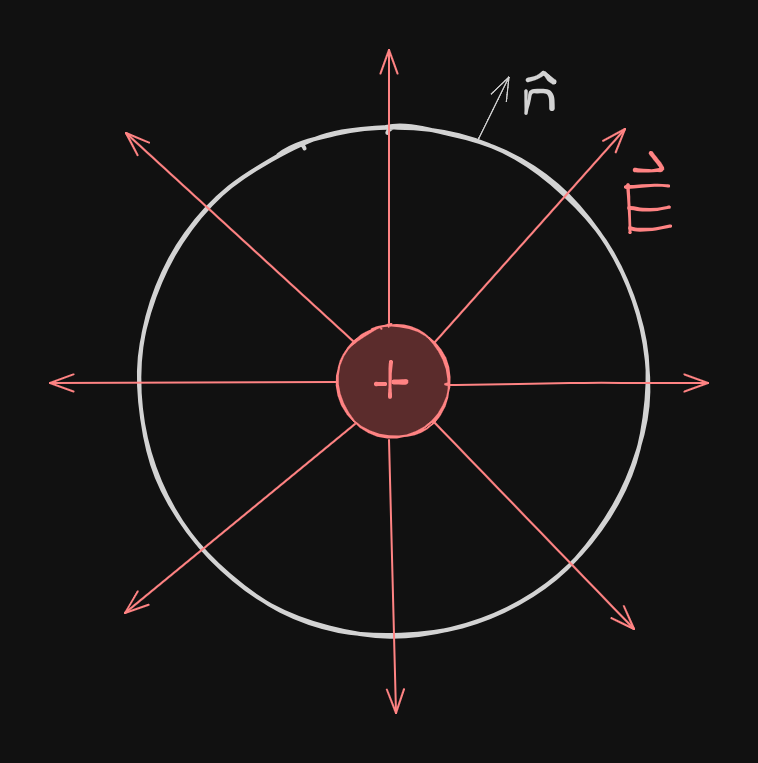
Then plugging in terms for this surface into the electric flux equation, then cancelling.