Kirchhoff’s Laws are two laws used to analyze complicated circuit.
Kirchhoff's Current Law
The current flowing into a node must equal the current flowing out of it.
For example:
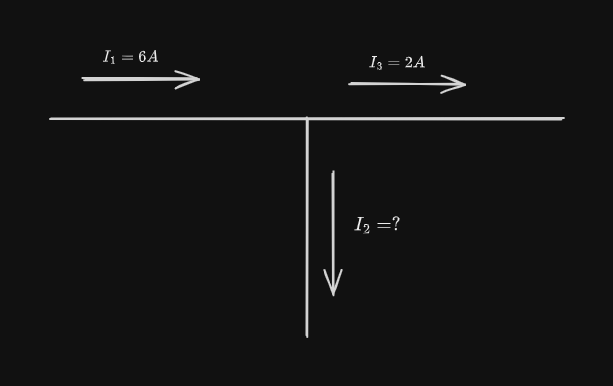
The other law is:
Kirchhoff's Voltage Law
The sum of all voltage differences around a closed loop is zero.
For example, with the circuit below:

We can find the missing resistance by using Kirchhoff’s Voltage Law.
- Pick an arbitrary point on the loop. Here, we will pick point
. - Move along the loop, adding and subtracting voltages until we have completed the loop.
- Add the voltage of the battery, since voltage increases as we move from the negative to positive terminal.
- Use Ohm’s Law to subtract the voltage drop at the resistor.
- Subtract the voltage of the second battery, since we are going from the positive to the negative terminal.
- Use Ohm’s Law to subtract the voltage drop from the second resistor.
- Set equal to zero and solve.